

plasma membrane, one or more chromosomes, cytosol, and ribosomes.

that gene, such as a protein that turns a gene on or off Name four structures found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Information flow: Nucleic acids are information storage molecules, and the information of genes is stored as a precise nucleotide sequence. Your genetic legacy is contained within the sequence of nucleotides on your chromosomes. The relationship of structure and function: the specific structure of a polysaccharide (how the monosaccharide monomers are joined together) affects the function of that polysaccharide. Both starch and cellulose consist of joined monosaccharide monomers, but the way that they are joined makes starch digestible by humans and cellulose not. DNA is usually double stranded, while RNA is usually single stranded What is the structure of a gene? What is the function of a gene? Structurally, a gene is a long stretch of DNA, functionally, a gene contains the information needed to produce a protein Plants use glucose as both a source of energy for cells and as a building block of their bodies pathways that transform energy and matter: the energy within a molecule of glucose can be transformed to promote cellular work, and the matter within glucose can be used to build large molecules such as starch. both use A,C, and G bases Name three differences between DNA and RNA -DNA uses T while RNA uses U as a base both have the same phosphate group along the backbone

A shortage of phosphorus in the soil would make it especially difficult for a plant to manufacture DNA A glucose molecule is to BLANK as a nucleotide is to a BLANK starch (or glycogen or cellulose) nucleic acid Name three similarities between DNA and RNA - Both DNA and RNA are polynucleotides
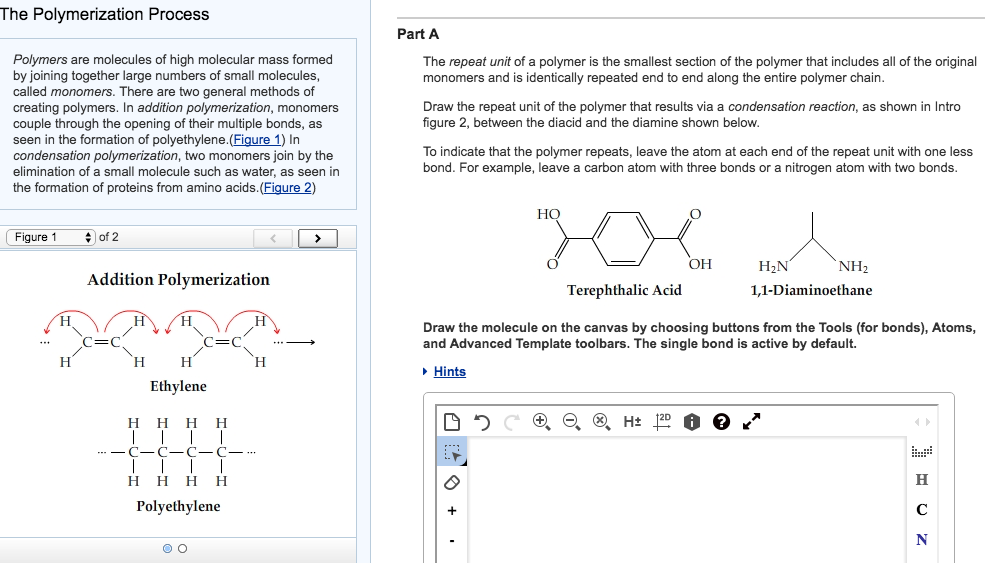
Where in the shape of a protein would you find hydrophobic amino acids? Hydrophobic amino acids are most likely to be found within the interior of a protein, far from the watery environment. Most proteins can easily dissolve in water. Humans and other animals can not digest wood because they BLANK Lack the enzyme needed to break down cellulose Explain how it could be possible to change an amino acid within a protein but not affect that proteins function If the change does not affect the shape of the protein in anyway, then that change would not affect the function of the protein. Saturated fats contain the maximum number of hydrogens along the tails. What is the formal name of the resulting molecule? fatty acid glycerol triglyceride Which of the following statements about saturated fats is true? b. disaccaride b When two molecules of glucose (C_6H_12O_6) are joined together by a dehydration reaction, what are the formulas of the two products? (Hint: No atoms are gained or lost.) C6H12O6+C6H12O6->C12H22O11+H2O One molecule of dietary fat is made by joining three molecules of BLANK. Such a reaction consumes a molecule of BLANK hydrolysis Which of the following terms include all the others in the list?ĭ. water Polymers are broken down into monomers through the chemical reaction called BLANK. Monomers are joined together to form larger polymers through BLANK, such a reaction releases a molecule of BLANK -Dehydration reactions How can you explain the differing effects of the two isomers? Isomers have different structures, or shapes, and the shape of a molecule usually helps determine the way it functions in the body. DNA contains BLANK polynucleotide strands, each composed of BLANK kinds of nucleotides (provide two numbers) two, four If one DNA strand has the sequence GATTGC, what is the sequence of the strand? CTTACG Complete this biologist pick up line: "Of all the nucleic acids, RNA is my favorite because its got BLANK in it!" U One isomer of methamphetamine is the addictive illegal drug known as "crank." The other is a medicine for sinus congestion. How can changing an amino acid alter the function of a protein? Changing an amino acid may alter the shape of the protein, which changes its function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
